This document explains how to:
- Get and install the NDK.
- Configure your system and the Eclipse and the Android Development Tools (“ADT”) for use with it.
- Verify, using a simple sample, that everything is working as expected.
Note that this document assumes that you are already familiar with Java-based Android development. For more information on that topic, see the Android developer site.
Installation
To install and configure the NDK, follow the steps below:
- To use the NDK, you must first have the Android SDK installed.
- Next, download and unzip the NDK, making sure to download the correct version for your development platform. You may place the unzipped directory anywhere on your local drive.
- If you are building from the command line, open a terminal window, and update your
PATHenvironment variable with the location of the directory that contains the NDK.
-
For example, in bash:
-
export PATH=$PATH:~/Android_SDK/NDK/
-
Or, in Windows:
-
set PATH=%PATH%;C:/Android_SDK/NDK/android-ndk-r10
Configuring Eclipse
Eclipse must know where the NDK is in order to use it when building your app.Follow these steps to set the location of the NDK:
- Launch Eclipse, which is installed as part of the Android SDK.
- Open Preferences.
- In the pane on the left side of the Preferences window, select Android > NDK. The Android section expands, revealing a number of subsections.
- Select NDK. In the pane on the right side of the Preferences window, browse to the directory that contains the NDK.
- Click OK to return to the Package Explorer display.
Verification
Eclipse
To confirm that you have installed the NDK, set it up correctly, and properly configure Eclipse, follow these steps:
- Import the hello-jni sample from `<ndk>/samples/’, as you would any other Android project.
- In the Project Explorer pane, right-click the project name (HelloJni). A context menu appears.
- From the context menu, select Android Tools > Add Native Support, as shown in Figure 2. The Add Android Native Support window appears.
- Accept the default library name (“hello-jni”), and click Finish.
- Build and execute the application.
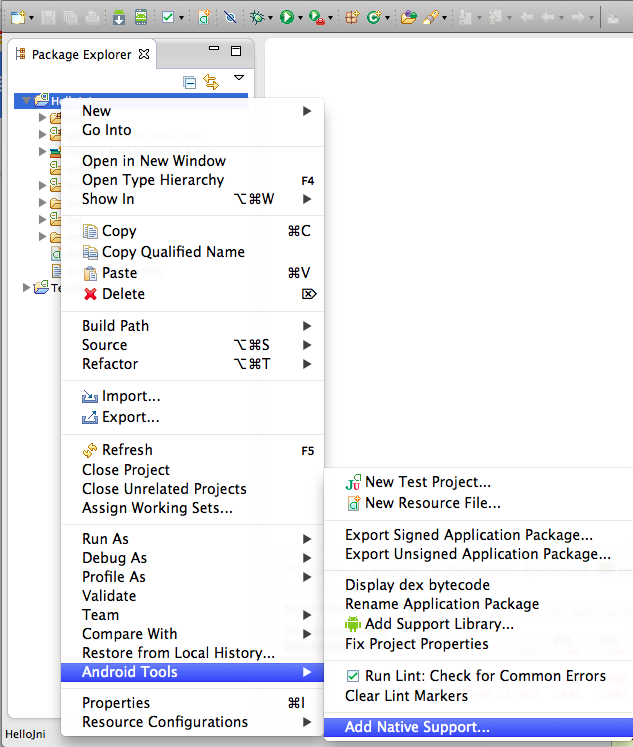
Figure 1. Adding native support to your project
Command line
Follow these steps to build from the command line:- Change to the root directory of your project.
- Execute ndk-build to build the native component of your app.
- Build and install your project as you would a regular Android app written in Java. For more information, see Building and Running and Building and Running from the Command Line.
$ ndk-build
If you have successfully installed and configured the NDK, the screen on your target device looks as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 2. Target-device screen after successful launch
 1.8.5
1.8.5